South Yorkshire’s past, present and future: what does the data say?
Written by Dan Olner
Dan Olner is a Policy Fellow for Y-PERN, South Yorkshire Mayoral Authority and Sheffield University Management School. Dan is an expert on economic and quantitative geography, data science, politics and international relations.
The Sheffield Political Economy Research Institute (SPERI) at Sheffield University have organised a set of seminars digging into the political economy of South Yorkshire, bringing together researchers and policymakers to better understand where the region has come from, where it is now and what the future holds.
In the first session, which took place on 5th March 2025, James Evans talked through some of the region’s historical data. James spoke about 1921, when Sheffield was the most heavily industrialised city in the UK. During this period up to the 1960’s employment in coal mining shrank while metalwork jobs carried on rising. In this time, most of the jobs growth happened away from cities, in surrounding towns – often making those towns reliant on a few large employers. This meant that from the 1970s onwards when employment began to retreat across the entire of the UK, some places were more vulnerable than others.
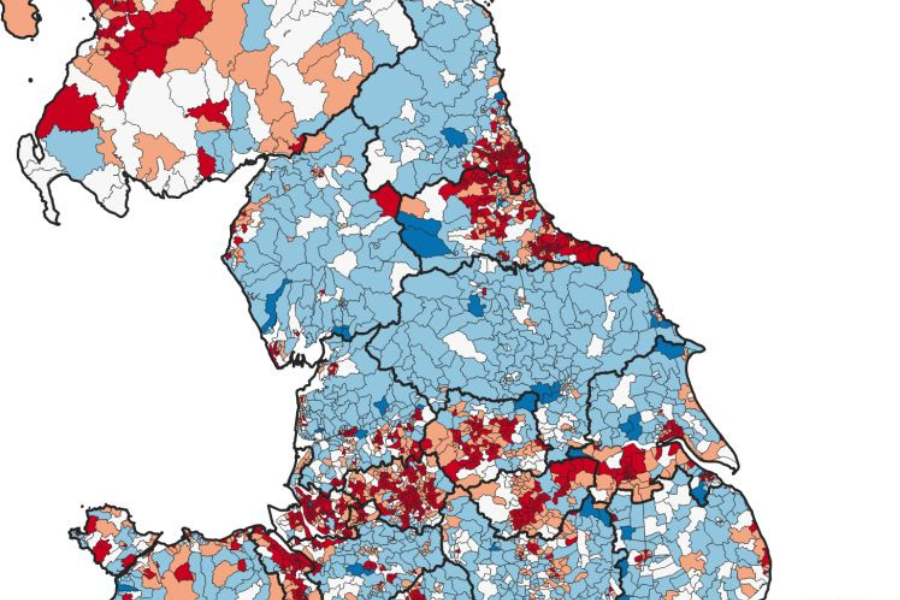
During the seminar, James discussed a typology of surviving versus declining places. Surviving places, more resilient because they were more economically diverse, could adapt. Those in the declining category, including places that had become more economic monocultures, were vulnerable. Impacts on these areas are still visible today in the deprivation data.
I (Dan Olner) then discussed 1970s and beyond, using Census data to dig further into just how profound the employment impacts were during that decade, and how certain parts of the country – including South Yorkshire – missed out on much of the bounce back that took place in the 80s.
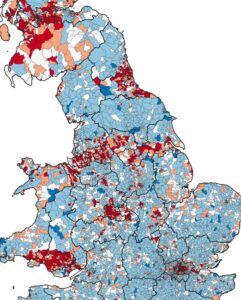
From the late 90s onwards, detailed regional productivity data paints a picture of continued structural change in the UK. While manufacturing shrunk and services grew in this period across the entire of the UK – continuing the same decades-long process of deindustrialisation – it was sectors concentrated in the North (like manufacturing) that declined most as a proportion of the UK economy. And whilst more recently there have been positive signs of jobs and output growth in Yorkshire, the region’s difficult economic history is still visible in its struggling productivity levels and low skills equilibrium.
This very broad-brush picture doesn’t tell the full story, however. Economic Innovations are taking place that cross sectoral boundaries; for example, those being celebrated at the Digital Forge, are blurring the difference between technology and manufacturing. The region’s devolved organisations are building plans that aim to benefit everyone – SYMCA’s plan for good growth aims to invest in both economic infrastructure and communities; South Yorkshire’s Integrated Care Strategy builds on deep data analysis to identify vital links between the wider determinants of health and economic outcomes.
The seminars into South Yorkshire’s political economical history will hopefully be the foundation to develop practical, policy relevant research that can contribute to helping the region navigate 21st century challenges.
The upcoming sessions will explore inequality, social change and devolution and will take place in person at the University of Sheffield. Contact [email protected] for further information.
You can view the slides from the first seminar here >